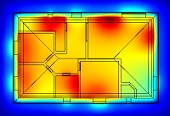
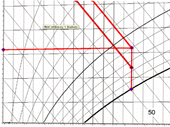
This article presents monitoring of internal heat-humidity microclimate in the bathroom of a typical family house. The text presents the results of measurement confronted with the requirements of current legislation. Temperature and humidity are the basic components of internal microclimate and as such contribute significantly to indoor air quality in residential and civic buildings. If the measured room bathrooms, whose character says that it will lead to significant gains water is then necessary to pay attention to the humidity. This may be their high value negatively affect the health of users indirectly by creating conditions for development of microorganisms and fungi. High humidity also has influence on some structures, the sensitivity to this aspect of the microclimate of a variant of the materials vary. The text presents the results of measurements which took place from 19.02.2011 to 06.14.2011.
Archiv článků od 16.1.2012 do 11.6.2012
Concept of energy efficiency buildings provides provable reduction in consumption of energy in compliance with the required user’s comfort. Taking into the account the trend to minimize heat escape and heat loss and increase of the airtight buildings, the installation of controlled ventilation is one of the steps leading to the optimal sanitary requirements and the overall energy efficiency of buildings. Quality indoor environment of energy efficient buildings, as well as the maximum level of comfort in this case is a controlled ventilation system with heat recovery and hot air heating. This article presents partial monitoring in situ measurements of selected parameters of the indoor environment during the operation of the upper and lower distribution system of hot air heating and ventilation in the selected experimental building.
The topic area of this article continues in focusing to noise and control properties of round dampers in HVAC systems. The acoustic and hydraulic properties of the round damper and systems of two dampers lined in series with a differently designed control flap under the pre-defined conditions are presented herein in mutual relationships. Authors submit recommendation as to the selection of a suitable damper type with respect to the noise lowering and good control abilities.
Less experienced operating managers in the branch of mechanical services of building can easily get difficulty in identifying the causes of technical problems, which sometimes a common practice brings. The article gives a table of causes and effects of defects and disorders related to cooling and heat sources.
Thermal stability of rooms without air-conditioning depends mainly on the thermal energy storage capacity of envelope and possible heat gains. Sensible heat storage structures, e.g. brickwork, concrete walls and slabs, usually do not have sufficient thermal storage capacity and some additional thermal storage mass is needed for cold storage. Passive cooling with thermal storage in phase change materials (PCMs) is a very effective way to improve thermal stability of the rooms with light-weight envelope. The main advantage of the phase change materials storage in buildings is the possibility to store a huge amount of heat in a rather narrow temperature interval. Passive cooling based on the latent heat storage technology can contribute to the energy and operative cost savings during summer season. The efficiency of this kind of passive cooling significantly depends on the heat transfer rates between the ambient environment and the thermal storage material. Modern administrative buildings or wooden buildings are often made of light-weight materials with rather small thermal mass. The latent heat cold storage in the phase change materials seems to be quite promising in this respect since it offers high thermal storage capacity.
The author brings the fundamental view concerning the problem of ventilation in residential buildings with respect to the building fire protection, in his contribution. No each designer or supplier of air conditioning systems designed for use in multiple dwelling or family houses is aware of this aspect importance and adheres it in the required level. He introduces interested parties with the substantial requirements that must be solved and taken into consideration, in the article.
Wide range of air cooled Compact Heat Exchangers is used in Heating, Ventilating, Air-Conditioning and Refrigeration industry (HVAC-R). Compact heat exchangers large air side area is characteristic for air cooled condensing units. Comparison includes 3 types of cross flow heat exchangers. These are expanded copper round tube on aluminium fin, expanded aluminium round tube on aluminium fin and extruded aluminium multiport flat tube heat exchanger with corrugated aluminium fin. Compactness of heat exchanger, pressure losses or its performance is in many cases the decisive parameter for customer choice. An article compares these parameters on various cross flow heat exchanger types in performance ranges 5kW and 60kW. Performance is measured in ambient temperature conditions of 25°C, due to the 40°C of condensing temperature and azeotropic refrigerant R404A, which is common medium for Air Conditioning systems. Selected performances are chosen to compare results on real applications, which is house air-conditioning unit at first case and bigger one for residence air-conditioning system or small industrial cooling.
The amount of volume coefficient depends on elevation of location of gas consumption and the temperature of gas flowing through the gasometer. In this paper we describe the procedure by which you can check that the coefficient of volume on the invoice is correct. The coefficient is one of the factors that affect your cost of gas.
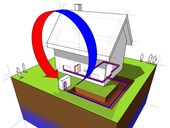
The article deals with the introduction of underground heat exchanger for preheating and precooling air for buildings. The introduction is devoted to the description of the system and its individual components and parameters that influence the behavior and performance of the system most. The second part presents a simple model, where you can see how each change affects the actual parameters of heat and cold, which can be gotten from the system.
This is a highly relevant article dealing with the comparison of two types ventilation - Natural ventilation through windows and controlled mechanical ventilation. The issue of ventilation in renovated homes in our country is still relevant. This paper describes a broad-based experiment measuring the intensity and quality of ventilation in two almost identical apartment houses. The conclusion confirms the well-known experience that controlled ventilation provides both - improved indoor air quality and the energy savings.
Inadequate ventilation is risky in connection with the pollutants indoors as there is no other way to dilute them. Indoors sources can produce allergens ( pets, house dust mites), toxic compounds like toluene or carbon monoxide, carcinogenic substances (e.g. benzene, formaldehyde etc.) and also such environment is ideal for spreading of infectious agents from the human sources (e.g. pandemic flu) or from the ventilation system (e.g. Legionella). Adequate ventilation is mostly the only way to improve the indoor environment and decrease health risks.
The article deals with the description of possible solutions to the specific problem of air with respect to existing installed equipment and climatic conditions that were in August this year. The article shows the importance to outdoor weather conditions on the operation of HVAC equipment and its design. Real running back shows problems in equipment design.
Supply of gas or electricity is so important that many customers do not want to risk a possible interruption when changing suppliers. New legislative rules defined in an amendment to the Energy Act No. 458/2000 Coll. (as amended by Act No. 211/2011 Coll.) but fill existing gaps in legislation and establish a procedure for changing supplier.
The paper describes basic principles, advantages and limitations of the air conditioning of buildings by adiabatic cooling. The principle of adiabatic (evaporative) cooling is the conversion of sensible heat to heat coupled with evaporation. Water sprayed into the air evaporates and the air temperature decreases and humidity increases.
The requirements for ventilation of residential buildings according to the standard ČSN EN 15 665/Z1
The ventilation rate in residential buildings is very discussed in present. The situation was complicated by missing or inaccurate requirements in legal regulations and technical standards. In February 2011 came into force on the national annex Z1 of European standard EN 15 665, which defines requirements for ventilation of residential buildings and also recommend suitable ventilation systems. Article briefly informs about the contents of the National Annex.
Regular inspection is focused to the boiler, smoke flue and accessories condition, its security and regulation. In addition to the technical condition and maintenance, the documentation, operating instructions, manuals and other documents are under inspection. It quantifies the overall boiler efficiency of measurement results, sets reference respectively minimum boiler efficiency and suggests possible actions.
In industrial plants, in case of fire there is accumulation of smoke that endangers the user object. Under these conditions the building must be opened to the smoke can ventilate out into the atmosphere, and that firefighters could enter the building. However, this opening causes the new oxygen support combustion. It is also one of the reasons why firefighters recommend the use fire damper with automatic controls and other devices (eg, smoke curtains, screens, blinds, etc.) as soon as possible after the beginning of fire, so as to prevent any accumulation, and that remove heat and smoke. This paper deals with the equipment for smoke and heat outlet.
zpět na aktuální články