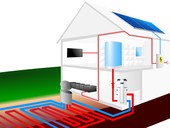
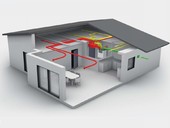
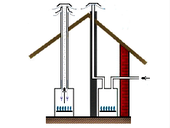
Ventilation infiltration in the form of leaking windows, doors is associated with unwanted heat leakage in cold periods. The size of the leakage depends on both the intensity of ventilation and the amount of energy contained in the air. The calculation should include not only the specific heat capacity of the dry air, but also the energy contained in the water vapor in the air.
Archiv článků od 24.2.2020 do 31.1.2022
The presented paper deals with the evaluation of the indoor environmental quality (IEQ) in two apartment units in different stages of interior construction - in the initial state and in the final state of a completely furnished apartment. The results of IEQ monitoring confirmed the minimal differences between an unfurnished apartment and a fully furnished apartment in terms of thermal-humidity microclimate. The average particulate matter concentrations of the two representative fractions (PM2.5 and PM10) were higher for apartment in the initial state. On the contrary, higher concentrations of total volatile organic compounds (TVOC) were recorded in the case of a furnished apartment. The legislative limit for PM10 (50 µg/m3) and the maximum recommended Mølhave value (200 µg/m3) for TVOC were exceeded several times in both apartments. In the case of unfurnished apartment, workers are exposed not only to increased concentrations of TVOC, but also to increased concentrations of PM, and should therefore pay attention to the protection and safety of health at work. More detailed monitoring aimed at identifying and determining the target VOCs showed the presence of xylenes and ethylbenzene in the indoor air of an unfurnished apartment. In addition to xylenes and ethylbenzene, toluene was present in the furnished apartment. Concentrations of these compounds were below legislative limits, except for ethylbenzene, for which no legislative limits are set. It follows from the above that further surface treatment and furnishing of the apartment contributes to increasing the level of VOCs in the indoor environment.
The heat pump with earth wells is a source of heat and cold for a university building in the center of Prague. Analyzes of measured data from the operation of this system are performed and the issue of parallel production of heat and cold in the context of sustainable development and buildings with minimal energy consumption is discussed.
High quality of the indoor environment expressed by indicators such as air temperature, relative humidity, concentration of carbon dioxide, or lighting has great impact on human health, comfort and performance. Therefore, the contribution focuses on the effect of an increase in indoor temperature on energy consumption.
The low heat loss in family houses enables comfortable hot air heating with air-to-air heat pumps. The authors give an example of the conditions for obtaining a subsidy from the „Nová Zelená úsporám“ (Green to Savings) program. Achieving the highest category of the NZÚ subsidy is also realistic in the „new buildings“ category.
Internal sewers can be a source of odors in a building. The penetration of odorous gases into the interior is prevented by suitably designed ventilation of sewers and installation of odor traps (slang called siphons). The article summarizes the causes of odor penetration and the principles of sewer ventilation design.
The pressure losses in the fittings are difficult to calculate in the design phase, as the key factor for them is the pressure losses, which is variable with respect to the type of fitting and its geometry. The possibility of obtaining an approximate value of the pressure loss coefficient is experimental measurements.
Minimum efficiency of heat recovery in ventilation with regard to energy balance and economic return
The minimum efficiency required for the efficient use of the heat exchanger in the equal pressure ventilation system of a family house is determined by the ratio of energy for fan operation and preheating to recovered energy, the balance in terms of energy and primary energy prices and economic return.
Development of the second generation of Eurocodes for climatic actions in the framework of the technical subcommittee CEN/TC250/SC1 is nearly finished. Revised Eurocodes should be more transparent, user-friendly and provide information about the basis of climatic actions and their effects on structures. National selection of the National Determined Parameters is expected to be given in the National Annexes including updated climatic maps.
The cause of the odor after the generational replacement of the gas boiler can be reduced air exchange in the room, improperly designed waste pipes, or even insufficient hygiene. The level of cleaning and hygiene is solved by the apartment user. Sufficient ventilation and treatment of the waste pipe, such as the installation of an aeration valve, should be designed by a person skilled in the art.
Today, technical support is an essential part of services related to the sale of products, heating technologies, including other parts of the HVAC area. It has a pre-sale, sales and post-sale form. For those who need to use support, they are intended in the article of the said advice. At the same time, however, companies that introduce support can learn or inspire changes that have already been implemented.
The paper focuses on the issue of one of the parameters of the indoor environment, which is the quality of indoor air. The new construction of an apartment building with controlled ventilation in the nZEB standard outlines the possible causes of perceived deteriorating air quality, but also the possible consequences associated with the construction of buildings with almost zero energy consumption in this area.
In connection with the entry into force of Decree No. 264/2020 Coll., On the energy performance of buildings, the method of assessing the energy performance of new buildings is changing. The article on the case study of a family house presents an approach to the concept of technical systems of new family houses from the point of view of current and future requirements (from 1. 1. 2022) for the energy performance of buildings.
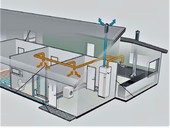
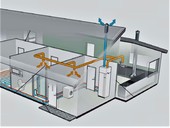
The subject of the research is a ventilation unit with a heat pump providing vacuum ventilation in a specific family house. The year-round energy balance of the operation was prepared from the obtained parameters. For a total heat loss of 5 kW, the seasonal heating factor SPF of the entire system was evaluated at the level of 2.5.
Due to long term cooling of the ice ring it may happen that subsoil was affected, bulged and consequently nonreturnable destroyed in case the structure was built on high-risk soil. Sub-soil heating system was tended to be prevention of undercooling and step-by-step freezing of subsoil. Purpose of the paper is evaluation of heat flow in the structure depending on heating fluid temperature and thermal insulation thickness.
zpět na aktuální články